Lower back pain occurs quite often. Patients say, "I have a sore lower back", "pinched waist", "cross back". If the pain is thoughtless, I can't say, "sore back", "pull back," "sore back". Sometimes the pain is described as burning in the lower back.
The lower back is called the lumbar spine - the place where in the end the ribs to the coccyx. Perhaps a separate word refers to the waist was necessary to determine the place where it hurts. After all, if the back pain, in most cases, the pain was back.
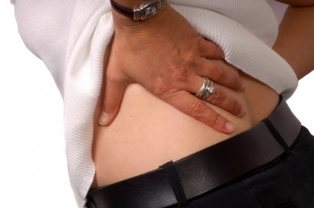
Which can be a pain
Most often, back pain occurs suddenly and sharply, acute. In this case we speak of lumbago (obsolete folk name cross). The pain is described as sharp "shooting". The movement of the bound, sometimes even impossible to straighten his back. At any movement the pain increases.
Pain may last a few minutes, and it can take considerable time (several days). It may be that the attack happened, and the pain more about yourself remind, but often the pain will return and the person gets used to that lower back can hurt.
Lower back pain can be not only sharp (sharp), she can use the drag character and be chronic. Mild but constant pain in spine, sometimes worse, for example during physical exertion, infectious diseases, colds, etc., is called the lumbar region. Sometimes does not happen directly, but is stored in the lower back stiffness the patient is experiencing discomfort.
Causes of lower back pain
Lower back pain can be caused by different reasons, but the statistics is as follows:
- In 90% of cases the pain is caused by problems with the spine and back muscles;
- 6% cause of pain is a kidney disease;
- 4% - diseases of other internal organs (urinary system, colon).
The proportion of the spine constitute the majority of all cases of back pain, and this is not a coincidence. In humans, the focus of the body is only at the level of the waist, and walked the whole burden almost entirely falls on the lumbar vertebrae (animals that move on four legs, this is not a problem). And when a person sits down, the lumbar vertebrae and the sacrum are experiencing the same force, the pressure which the diver weighs 170-meter layer of water. Naturally, this area is particularly vulnerable.
Diseases of the musculoskeletal system, causing lower back pain:
- a pinched sciatic nerve. Nerve roots extend from the spinal cord are squeezed by the adjacent vertebrae. When this happens, a sharp, shooting pain. Typically, the harassment of the roots becomes possible as a result of degenerative changes in the spine (osteochondrosis): the intervertebral discs that separate the vertebrae from each other is destroyed, the gap between the vertebrae narrows and sudden movement (tilt, rotation) can lead to a pinched nerve branch;
- sciatica (sciatica). Pinched nerve roots can become inflamed. Inflammation of the nerve roots is called sciatica (from lat. radicula - "root"); can indicate inflammation of the sciatic nerve is sometimes used as a specific name - sciatica. With the defeat of the sciatic nerve can be lumboischalgia - low back pain, spreading in the thigh and foot during the sciatic nerve;
- herniated disc - protrusion of a fragment of the intervertebral disc into the spinal canal. Occur as a result of injury or degenerative changes in the spine (osteochondrosis);
- myositis of the lumbar muscles. Myositis is inflammation of muscles. The reason for myositis of the lumbar muscles can be hypothermia or sudden excitement.
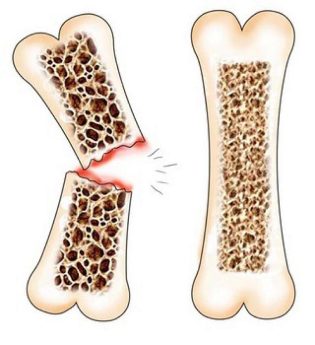
Also lower back pain can be caused by such diseases as multiple sclerosis, degenerative sacroiliitis, osteoporosis.
Prevention of back pain
The occurrence of lower back pain is often triggered by a careless attitude to their own health. The pain may be due to:
- long-term stay in the same position (for example, sedentary work);
- bad posture;
- low mobility;
- excessive physical exertion.
All of these factors contribute to the development of the disease, which is manifested by pain in the lower back. Risk pain can be reduced, if you follow the following tips for physicians:
- follow the carriage;
- avoid awkward postures at work sitting. It is desirable that the knee was slightly higher than the hip joints. Use a small chair or stand on his feet. Make a small pillow between the lower back and the seat back;
- when sedentary work is from time to time to get up to move. Do it every hour, five-minute breaks; how to lift weights
- it is desirable to sleep in the premium bedding-the mattress of bed-mattress (elastic and tough enough);
- lift weights, is necessary, because bending the knees, not the back. That is, you need to sit down, bending your knees and then straighten them while maintaining a straight line of the back;
- the cargo, it should be evenly distributed between both hands to carry the whole load with one hand (one heavy bag);
- every day you should do a set of exercises aimed at strengthening muscles in the abdomen and back.
Lower back pain kidney disease
When back pain is important to determine what the cause of the pathology of the musculoskeletal system or a disease of the kidneys (and other organs). Diagnostics is the task of the doctor. However, there is evidence that pain can be caused by problems with the kidneys or (and) other organs of the urogenital system. The manifestation of these symptoms it is advisable to consult a doctor-urologist. Kidney disease (or wider - the genitourinary system) can be suspected, if the pain is accompanied by:
- A general weakening of the illness (lethargy, drowsiness, weakness, fatigue);
- of the eyelids, face. Swelling is particularly pronounced in the morning after waking, and subsides by day's end;
- body temperature increased, chills, sweating;
- loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting;
- increased or painful urination;
- the change in the characteristics of urine (it can become more concentrated in color-or vice versa - is a colorless, contains mucus or blood);
- increase in blood pressure.
Also an important sign that lower back pain caused by problems in the internal organs, and not the musculoskeletal system is its independence of the position of the body: changes in body position and limb pain is not amplified and not reduced. However, with a long-term stay upright pathology examination, the pain can get worse. Is the value and localization of pain. If you have kidney disease the pain is often observed on the one hand (since usually suffers from only one kidney). Kidney pain can be limited to the lower back, and spread during the course of the ureter to the groin, external genitals, inner thighs.
Sore lower back: what to do?
Lower back pain is a symptom of a disease that requires treatment. Therefore, it is necessary to consult a doctor. But if a sudden attack of acute pain ("lumbago" typical sciatica), we must first ease the pain. Doctors advise:
- use a little warm. Tie the waist woolen scarf or a woolen belt;
- take the pain;
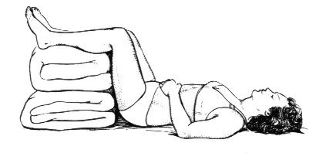
- you must take a posture that allows you to relax your back muscles. It is recommended to lie on your back on a hard flat surface (Board); the foot should be raised and bent at the knees, why it is necessary, so that they can put a folded blanket or pillow. (On the floor go desirable, you can blow out of the draft).
The proposed position is not a dogma. The patient should feel relieved, so there are other possible positions; for example, lying on the table put his legs bent at the knees, holding between the pillow. You can try to lie on your stomach and stretch your legs by placing a pillow under the ankle joints. If the sharpness of the pain is removed, this does not mean that the doctor is no longer needed. Without proper care, the scenes are repeated, and the situation is getting worse.
To what doctor to address a complaint of low back pain?
When back pain is best to consult a therapist, because, firstly, it is necessary to identify the disease, what organs, causing pain. Depending on the audit results, it may be necessary to consult a specialist. It can be shown:
- consult a neurologist for assessing the spine, back muscles and nervous system;
- consult a doctor-urologist if suspicion of disease of the urinary tract;
- consultation of the gynecologist - in case of suspicion or presence of chronic diseases of the organs of the female reproductive system;
- The most common blood test and urinalysis, to confirm or exclude the inflammatory nature of the disease;
- radiography of the spine ;
- Ultrasound of the hip joints ;
- as well as other studies.





































